什么是中断
一个线程不应该由其他线程来强制中断或停止,而是应该由线程自己自行停止。所以,
Thread.stop,Thread.suspend,Thread.resume都已经被废弃了。
在Java中没有办法立即停止一条线程,然而停止线程却显得尤为重要,如取消一个耗时操作。因此, Java 提供了一种用于停止线程的机制——中断。
**需要注意的是:中断只是一种协作机制, Java 没有给中断增加任何语法,中断的过程完全需要程序员自己实现。 **
Java 中如何优雅退出(中断)线程呢?
Java中退出当前的线程有三种常见方法:
- 使用 volatile 多线程之间的可见性
- 使用原子类 AtomicBoolean
- 使用中断 API interrupt() 搭配 isInterrupted()
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/**
* 使用 volatile 多线程之间的可见性
*/
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (volatileFlag) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",当前线程已经中断:volatileFlag = " + volatileFlag);
break;
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",hello volatileFlag = " + volatileFlag);
}
}
}, "线程1").start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
new Thread(() -> {
volatileFlag = true;
}, "线程2").start();
/**
* 使用原子类 AtomicBoolean
*/
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (atomicBooleanFlag.get()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",当前线程已经中断:atomicBooleanFlag = " + atomicBooleanFlag.get());
break;
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",hello atomicBooleanFlag = " + atomicBooleanFlag.get());
}
}
}, "线程3").start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
new Thread(() -> {
atomicBooleanFlag.set(true);
}, "线程4").start();
/**
* 使用中断 API interrupt() 搭配 isInterrupted()
*/
Thread thread5 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",当前线程已经中断:isInterrupted = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
break;
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",hello isInterrupted = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}
}
}, "线程5");
thread5.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
new Thread(() -> {
thread5.interrupt();
}, "线程6").start();
}
三种中断API比较
翻看 Java API 文档,我们可以看到,中断有三个方法。
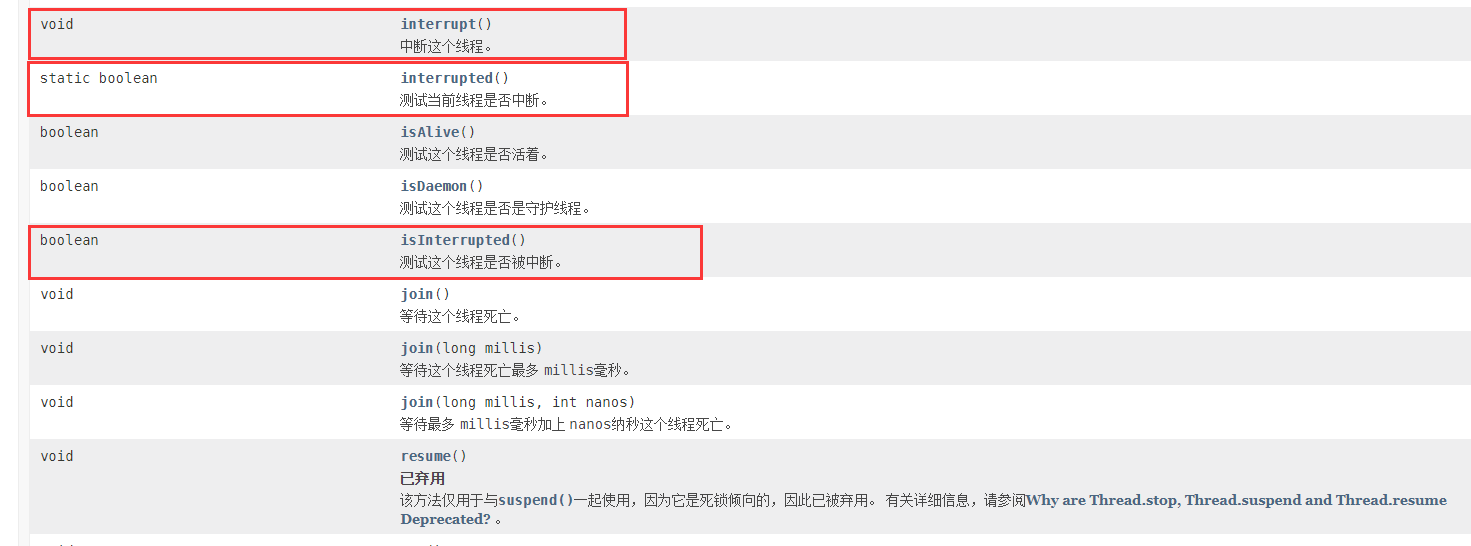
- void interrupt()
- static boolean interrupted()
- boolean isInterrupted()
那这三个有什么区别呢?这三个又怎么用呢?顺便吐槽一句。这方法都起的什么鸟名字。
void interrupt() 和 boolean isInterrupted()
若要中断一个线程,你需要手动调用该线程的interrupt方法,但是该方法不会立即中断线程,只是中断协商的一个机制,只是把中断标识位由默认的false设置为true。
void interrupt():中断线程,不是真正的中断线程,而只是将线程中断标识位从false设置成true。
boolean isInterrupted():测试当前线程是否中断。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i<= 100; i++){
System.out.println("当前线程还存活:i = " + i);
}
System.out.println("打断之后且运行完成后线程的状态: " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}, "线程1");
thread1.start();
System.out.println("打断之前线程的状态: " + thread1.isInterrupted());
// 打断当前的线程
thread1.interrupt();
System.out.println("打断之后线程的状态: " + thread1.isInterrupted());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println("打断之后线程的状态再次观察: " + thread1.isInterrupted());
}
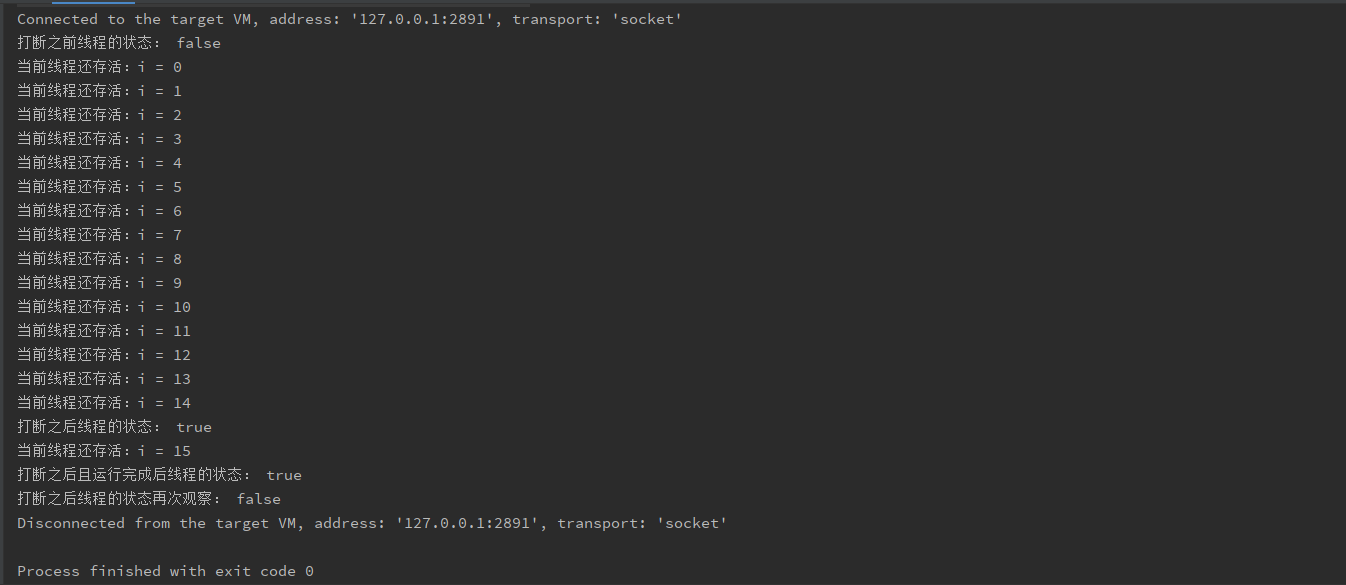
通过上面的程序,我们发现:
- 设置中断后,程序并没有立马就停止,而是继续运行。
- 当线程在活动状态时,线程还在运行执行中,thread1.isInterrupted() = true。当线程在非活动状态时,线程不在执行,已经结束thread1.isInterrupted() = false。
通过最上面的程序,我们的应用是可以跑的,但是为什么我加了一个Thread.sleep(500);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/**
* 使用中断 API interrupt() 搭配 isInterrupted()
*/
Thread thread5 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",当前线程已经中断:isInterrupted = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ",hello isInterrupted = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
}
}, "线程5");
thread5.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
new Thread(() -> {
thread5.interrupt();
}, "线程6").start();
}
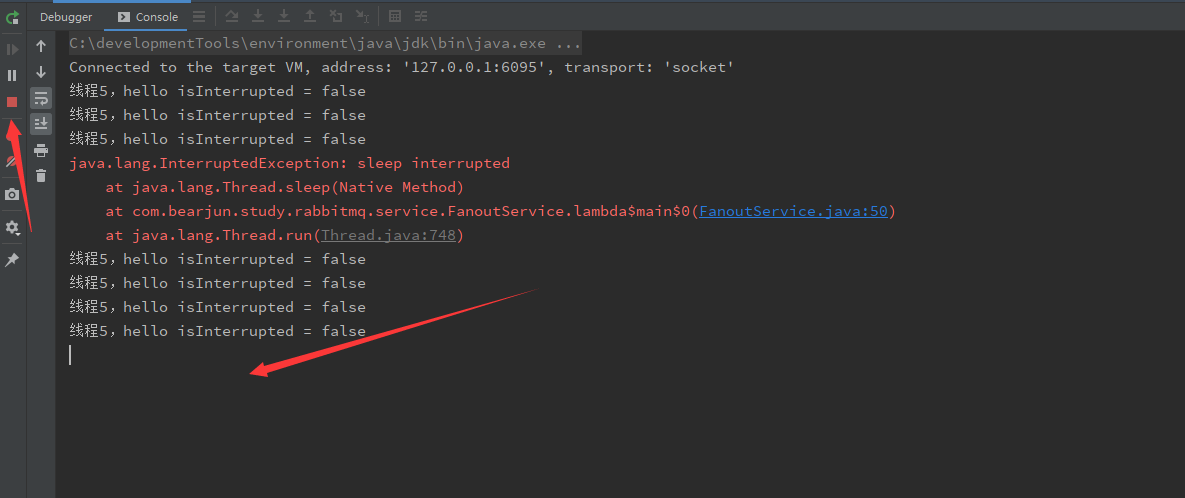
程序就停不下来呢?原来啊,interrupt()里面有一段这样的描述:
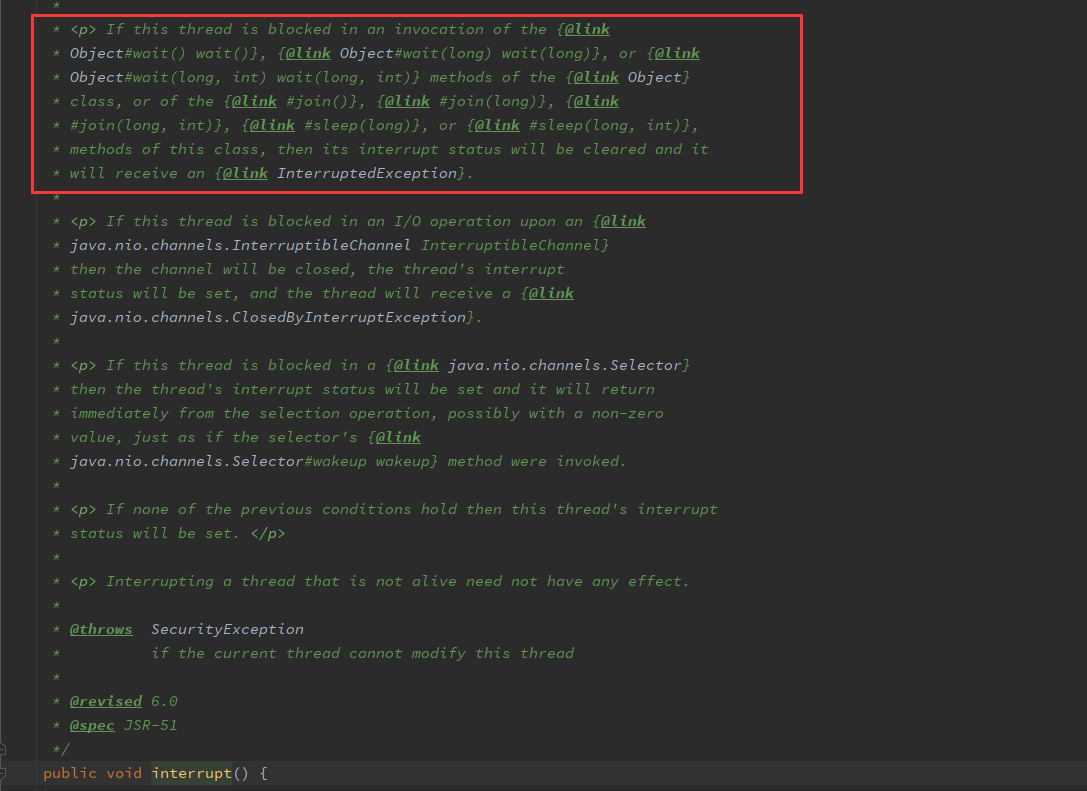
如果该线程阻塞的调用wait() , wait(long) ,或wait(long, int)的方法Object类,或者在join() , join(long) , join(long, int) , sleep(long) ,或sleep(long, int) ,这个类的方法,那么它的中断状态将被清除,并且将收到一个InterruptedException 。
那如果要停止怎么办呢? 很简单,只需要在 InterruptedException e 的 异常处理中添加Thread.currentThread().interrupt()就好了。
static boolean interrupted()
静态方法 Thread.interrupted():判断线程是否被中断,并清除当前中断的状态。
这个方法做了两件事情:
1、返回当前线程的中断状态
2、将当前线程的中断状态设置为false
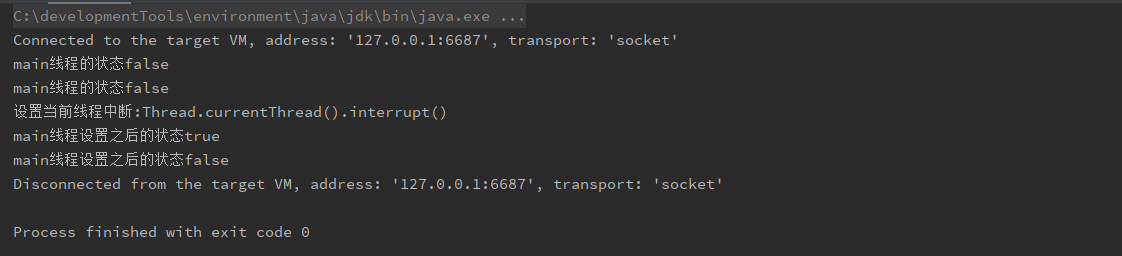
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程的状态" + Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程的状态" + Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("设置当前线程中断:Thread.currentThread().interrupt()");
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程设置之后的状态" + Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程设置之后的状态" + Thread.interrupted());
}
总结
- void interrupt():这只中断标识位为true,线程并不会立马停止。当遇到 InterruptedException 异常时,中断标识位会被重置为 false 。
- boolean isInterrupted():判断当前的线程是否被中断。
- static boolean interrupted():判断线程是否被中断,并清除当前中断的状态。




评论区